Q5® High-Fidelity DNA Polymerase
Product information| Code | Name | Size | Quantity | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
M0491S |
Q5 High-Fidelity DNA Polymerase |
100 units ( 2000 units/ml ) | - | Unavailable in your region | |
M0491L |
Q5 High-Fidelity DNA Polymerase |
500 units ( 2000 units/ml ) | - | Unavailable in your region |
Q5® High-Fidelity DNA Polymerase
Fidelity at its finest – for over 10 years This product is available in a glycerol-free format. Contact us for more information.
Product Introduction
Q5® High-Fidelity DNA Polymerase sets a new standard for both fidelity and robust performance. With the highest fidelity amplification available (~280 times higher than Taq), Q5 results in ultra-low error rates. Q5 is composed of a novel polymerase that is fused to the processivity-enhancing Sso7d DNA binding domain, improving speed, fidelity and reliability of performance.
Working with uracil-containing DNA templates or using dUTP? Learn about Q5U Hot Start High-Fidelity DNA Polymerase (NEB #M0515).
- Highest fidelity amplification (~280X higher than Taq)
- Ultra-low error rates
- Superior performance for a broad range of amplicons (from high AT to high GC)
- Also available: Q5 Hot Start standalone polymerase (NEB #M0493) and master mix formats (NEB #M0492, M0494)
| Catalog # | Size | Concentration |
|---|---|---|
| M0491S | 100 units | 2000 units/ml |
| M0491L | 500 units | 2000 units/ml |
Featured Videos
View Video Library-

Important Tips for Q5® Polymerase
-

Why Choose Q5® High-fidelity Polymerase?
-

Behind the paper: Examining Sources of Error in PCR by Single-Molecule Sequencing
-
Why is Tm Important in Primer Design?
-

Tips for Amplifying Large Amplicons
-

How to Amplify GC-rich DNA
-

5 Tips for Setting Up Your PCR
-
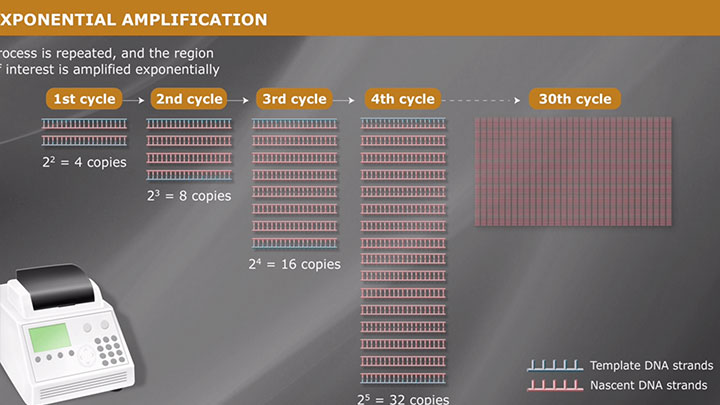
Overview of PCR
- Product Information
- Protocols, Manuals & Usage
- Tools & Resources
- FAQs & Troubleshooting
- Citations & Technical Literature
- Quality, Safety & Legal
- Other Products You May Be Interested In
Product Information
Description
Q5® High-Fidelity DNA Polymerase
is a high-fidelity, thermostable DNA polymerase
with 3´→ 5´ exonuclease activity, fused to a
processivity-enhancing Sso7d domain to support
robust DNA amplification. With an error rate ~280-fold lower than that of Taq DNA Polymerase, Q5 High-Fidelity
DNA Polymerase is ideal for cloning and can
be used for long or difficult amplicons. Q5
High-Fidelity DNA Polymerase is supplied with
an optimized buffer system that allows robust
amplification regardless of GC content. The 5X
Q5 Reaction Buffer contains 2 mM Mg++ at final
(1X) reaction concentrations and is recommended
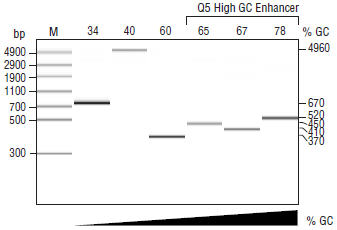
for most routine applications. For GC-rich targets
(≥ 65% GC), amplification can be improved by
the addition of the 5X Q5 High GC Enhancer. Q5
High-Fidelity DNA Polymerase is unlike typical,
lower fidelity PCR enzymes. To determine the optimal annealing temperatures for a given set of primers, use of the NEB Tm Calculator is highly recommended.
Product Source
An E. coli strain that carries the Q5 High-Fidelity DNA Polymerase gene.- This product is related to the following categories:
- Q5® High-Fidelity DNA Polymerases,
- This product can be used in the following applications:
- Gibson Assembly®,
- Long Range PCR,
- Fast PCR,
- High-Fidelity PCR,
- Multiplex PCR,
- DNA Amplification, PCR & qPCR,
- Specialty PCR,
- Routine PCR,
- PCR, Fast Cloning: Accelerate your cloning workflows with reagents from NEB
Reagents Supplied
Reagents Supplied
The following reagents are supplied with this product:
| NEB # | Component Name | Component # | Stored at (°C) | Amount | Concentration | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Properties & Usage
Materials Required but not Supplied
- Deoxynucleotide (dNTP) Solution Mix (NEB #N0447)
- Nuclease-free Water (NEB #B1500)
Unit Definition
One unit is defined as the amount of enzyme that will incorporate 10 nmol of dNTP into acid insoluble material in 30 minutes at 74°C.Unit Assay Conditions
25 mM TAPS-HCl (pH 9.3 @ 25°C), 50 mM KCl, 2 mM MgCl2, 1 mM β-mercaptoethanol, 200 μM dNTPs including [3H]-dTTP and 15 nM primed M13 DNA.Application Features
- High-fidelity PCR
- Cloning
- Long or Difficult Amplification
- High-throughput PCR
Related Products
Companion Products
Protocols, Manuals & Usage
Protocols
Usage & Guidelines
Application Notes
Tools & Resources
Selection Charts
Web Tools
FAQs & Troubleshooting
FAQs
- What are the advantages of using Q5® High-Fidelity DNA Polymerase?
- What are the differences between the numerous Q5® Polymerase products available?
- My results are not as expected. Where can I find troubleshooting help?
- What ends will my PCR products have?
- What does exonuclease activity mean for a DNA polymerase?
- Does Q5® High-Fidelity DNA Polymerase exhibit a strand displacement activity?
- What are the properties of this polymerase (fidelity, product ends, max amplicon, modified base incorporation, etc.)?
- How should I determine the appropriate annealing temperature for my reaction?
- What should the final primer concentration be in my PCR?
- When and how should I use the Q5® High GC Enhancer?
- Do other polymerases work in Q5® Reaction Buffer?
- There is a precipitate in the bottom of the buffer tube. Is this normal?
Troubleshooting
Citations & Technical Literature
Citations
Additional Citations
- Harish Nag Kankipati, Marta Rubio-Texeira, Dries Castermans, George Diallinas, Johan M Thevelein (2015) Sul1 and Sul2 Sulfate Transceptors Signal to Protein Kinase A upon Exit of Sulfur Starvation. J Biol Chem; 290, 10430-46. PubMedID: 25724649, DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M114.629022
- Amin Zargar, David N Quan, Milad Emamian, Chen Yu Tsao, Hsuan-Chen Wu, Chelsea R Virgile, William E Bentley (2015) Rational design of 'controller cells' to manipulate protein and phenotype expression. Metab Eng; , PubMedID: 25908186, DOI: 10.1016/j.ymben.2015.04.001
- Yonghe Zhang, Huiming Huang, Shanshan Xu, Bo Wang, Jianhua Ju, Huarong Tan, Wenli Li (2015) Activation and enhancement of Fredericamycin A production in deepsea-derived Streptomyces somaliensis SCSIO ZH66 by using ribosome engineering and response surface methodology. Microb Cell Fact; 14, 64. PubMedID: 25927229, DOI: 10.1186/s12934-015-0244-2
- Silva-Herzog E, McDonald EM, Crooks AL, Detweiler CS. (2015) Physiologic Stresses Reveal a Salmonella Persister State and TA Family Toxins Modulate Tolerance to These Stresses PLoS One; 12, PubMedID: 26633172, DOI: 10.1371
- Jun Wu, Daiji Okamura, Mo Li, Keiichiro Suzuki, Chongyuan Luo, Li Ma, Yupeng He, Zhongwei Li, Chris Benner, Isao Tamura, Marie N Krause, Joseph R Nery, Tingting Du, Zhuzhu Zhang, Tomoaki Hishida, Yuta Takahashi, Emi Aizawa, Na Young Kim, Jeronimo Lajara, Pedro Guillen, Josep M Campistol, Concepcion Rodriguez Esteban, Pablo J Ross, Alan Saghatelian, Bing Ren, Joseph R Ecker, Juan Carlos Izpisua Belmonte (2015) An alternative pluripotent state confers interspecies chimaeric competency. Nature; , PubMedID: 25945737, DOI: 10.1038/nature14413
- Longhai Dai, Can Liu, Yueming Zhu, Jiangsheng Zhang, Yan Men, Zeng Yan, Yuanxia Sun (2015) Functional Characterization of Cucurbitadienol Synthase and Triterpene Glycosyltransferase Involved in Biosynthesis of Mogrosides from Siraitia grosvenorii. Plant Cell Physiol; , PubMedID: 25759326, DOI: 10.1093/pcp/pcv043
- Yang YJ, Han YY, Chen K, Zhang Y, Liu X, Li S, Wang KQ, Ge JB, Liu W, Zuo J. (2015) TonEBP modulates the protective effect of taurine in ischemia-induced cytotoxicity in cardiomyocytes Cell Death Dis; PubMedID: 26673669, DOI: 10.1038
- Yuan Xue, Jossef Osborn, Anand Panchal, Jay L Mellies (2015) The RpoE Stress Response Pathway Mediates Reduction of the Virulence of Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli by Zinc. Appl Environ Microbiol; 81, 3766-74. PubMedID: 25819956, DOI: 10.1128/AEM.00507-15
- Christine Henke, Pamela L Strissel, Maria-Theresa Schubert, Megan Mitchell, Claus C Stolt, Florian Faschingbauer, Matthias W Beckmann, Reiner Strick (2015) Selective expression of sense and antisense transcripts of the sushi-ichi-related retrotransposon - derived family during mouse placentogenesis. Retrovirology; 12, 9. PubMedID: 25888968, DOI: 10.1186/s12977-015-0138-8
- Binyamin D Berkovits, Christine Mayr (2015) Alternative 3' UTRs act as scaffolds to regulate membrane protein localization. Nature; , PubMedID: 25896326, DOI: 10.1038/nature14321
- Wang XJ, Zhang XJ, Hu W, Zhang TY, Wang SQ (2014) A simple and efficient strategy for the de novo construction of greater-than-genome-length hepatitis B virus replicons J Virol Methods; 207, 158-62. PubMedID: 25025817, DOI: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2014.07.009
- Vidhyadhar Nandana, Sushant Singh, Abhay Narayan Singh, Vikash Kumar Dubey (2014) Procerain B, a cysteine protease from Calotropis procera, requires N-terminus pro-region for activity: cDNA cloning and expression with pro-sequence. Protein Expr Purif; 103C, 16-22. PubMedID: 25173974, DOI: 10.1016/j.pep.2014.08.003
- Martin Kostovcik, Craig C Bateman, Miroslav Kolarik, Lukasz L Stelinski, Bjarte H Jordal, Jiri Hulcr (2014) The ambrosia symbiosis is specific in some species and promiscuous in others: evidence from community pyrosequencing. ISME J; , PubMedID: 25083930, DOI: 10.1038/ismej.2014.115
- Bert De Rybel, Milad Adibi, Alice S. Breda, Jos R. Wendrich, Margot E. Smit, Ondej Novk, Nobutoshi Yamaguchi, Saiko Yoshida, Gert Van Isterdael, Joakim Palovaara, Bart Nijsse, Mark V. Boekschoten, Guido Hooiveld, Tom Beeckman, Doris Wagner, Karin Ljung, Christian Fleck, Dolf Weijers (2014) Integration of growth and patterning during vascular tissue formation in Arabidopsis Science; 345, 1255215. PubMedID: 25104393, DOI: 10.1126/science.1255215
- Xin Duan, Arjun Krishnaswamy, Irina De la Huerta, Joshua R Sanes (2014) Type II Cadherins Guide Assembly of a Direction-Selective Retinal Circuit. Cell; 158, 793-807. PubMedID: 25126785, DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.06.047
- Lieve Naesens, Luke Guddat, Dianne Keough, André B.P. van Kuilenburg, Judith Meijer, Johan Vande Voorde and Jan Balzarini (2013) ROLE OF HUMAN HYPOXANTHINE GUANINE PHOSPHORIBOSYLTRANSFERASE IN ACTIVATION OF THE ANTIVIRAL AGENT T-705 (FAVIPIRAVIR) Mol Pharmacol; 87247. PubMedID: 23907213
- Anastassia Voronova Erin Coyne, Ashraf Al Madhoun, Joel V. Fair, Neven Bosiljcic, Catherine St-Louis, Grace Li, Sherry Thurig, Valerie A. Wallace, Nadine Wiper-Bergeron, and Ilona S. Skerjanc (2013) Hedgehog Signaling Regulates MyoD Expression and Activity J Biol Chem; 288(6), 4389–4404. PubMedID: 23266826
- Hicham Bouabe, Klaus Okkenhaug (2013) A Protocol for Construction of Gene Targeting Vectors and Generation of Homologous Recombinant Embryonic Stem Cells Methods Mol Biol; 1064, 337-354. PubMedID: 23996269
- Wilber Quispe-Tintaya, Ryan R White, Vasily N Popov, Jan Vijg, Alexander Y Maslov (2013) Fast mitochondrial DNA isolation from mammalian cells for next-generation sequencing Biotechniques; 55(3), 133-6. PubMedID: 24003945, DOI: 10.2144/000114077
Feature Articles
Quality, Safety & Legal
Quality Assurance Statement
Quality Control tests are performed on each new lot of NEB product to meet the specifications designated for it. Specifications and individual lot data from the tests that are performed for this particular product can be found and downloaded on the Product Specification Sheet, Certificate of Analysis, data card or product manual. Further information regarding NEB product quality can be found here.Specifications
The Specification sheet is a document that includes the storage temperature, shelf life and the specifications designated for the product. The following file naming structure is used to name these document files: [Product Number]_[Size]_[Version]Certificate Of Analysis
The Certificate of Analysis (COA) is a signed document that includes the storage temperature, expiration date and quality controls for an individual lot. The following file naming structure is used to name these document files: [Product Number]_[Size]_[Version]_[Lot Number]- M0491S_L_v2_0051506
- M0491S_L_v2_0051512
- M0491S_L_v2_0051606
- M0491S_L_v2_0051612
- M0491S_L_v2_0051705
- M0491S_L_v2_0051712
- M0491L_v2_10012836
- M0491L_v2_10013562
- M0491S_v2_10012835
- M0491L_v2_10014691
- M0491L_v2_10015043
- M0491S_v2_10013927
- M0491L_v2_10015154
- M0491S_v2_10015250
- M0491S_v2_10018821
- M0491L_v2_10019448
- M0491S_v2_10021049
- M0491S_v2_10024156
- M0491L_v2_10019984
- M0491L_v2_10029548
- M0491S_v2_10029474
- M0491S_v2_10031845
- M0491L_v2_10031973
- M0491S_v2_10033011
- M0491L_v2_10034381
- M0491L_v2_10036736
- M0491S_v2_10034445
- M0491L_v2_10038573
- M0491L_v2_10041546
- M0491S_v2_10040030
- M0491L_v2_10043237
- M0491S_v2_10043730
- M0491L_v2_10045942
- M0491S_v2_10047029
- M0491L_v2_10047971
- M0491S_v2_10048423
- M0491L_v2_10050126
- M0491S_v2_10050124
- M0491L_v2_10054113
- M0491S_v2_10055289
- M0491S_v2_10056736
- M0491S_v2_10057468
- M0491L_v2_10056737
- M0491S_v2_10057803
- M0491L_v2_10057804
- M0491L_v2_10061017
- M0491S_v2_10061482
- M0491L_v2_10062501
- M0491S_v2_10064041
- M0491L_v2_10065838
- M0491L_v2_10070258
- M0491L_v2_10072372
- M0491S_v2_10069225
- M0491S_v2_10073430
- M0491L_v2_10075382
- M0491S_v2_10078214
- M0491S_v2_10079942
- M0491L_v2_10079278
- M0491S_v2_10082864
- M0491L_v2_10083602
- M0491S_v2_10085883
- M0491L_v2_10085771
- M0491S_v2_10088897
- M0491L_v2_10090382
- M0491S_v2_10092015
- M0491S_v2_10094117
- M0491L_v2_10094118
- M0491L_v2_10096298
- M0491S_v2_10097553
- M0491S_v2_10098100
- M0491L_v2_10098319
- M0491S_v2_10104077
- M0491L_v2_10104078
- M0491S_v2_10104378
- M0491L_v2_10108269
- M0491S_v2_10107555
- M0491L_v2_10108570
- M0491L_v2_10109793
- M0491S_v2_10110817
- M0491L_v2_10111133
- M0491S_v2_10114125
- M0491L_v2_10114515
- M0491L_v2_10117616
- M0491S_v2_10119105
- M0491L_v2_10120989
- M0491L_v2_10126940
- M0491S_v2_10127801
- M0491L_v2_10129201
- M0491S_v2_10129545
- M0491L_v2_10132246
- M0491S_v2_10134504
- M0491L_v2_10136934
- M0491S_v2_10137983
- M0491L_v2_10140937
- M0491G_v1_10142490
- M0491G_v1_10142618
- M0491S_v2_10140740
- M0491L_v2_10142619
- M0491S_v2_10145921
- M0491L_v2_10146683
- M0491S_v2_10148681
- M0491L_v2_10149307
- M0491S_v2_10152175
- M0491L_v2_10153112
- M0491G_v1_10149551
- M0491S_v2_10155247
- M0491G_v1_10158219
- M0491G_v1_10158513
- M0491G_v1_10159449
- M0491L_v2_10157263
- M0491S_v2_10162276
- M0491L_v2_10161628
- M0491G_v1_10163146
- M0491L_v2_10164962
- M0491S_v2_10164583
- M0491S_v2_10168850
- M0491L_v2_10168297
- M0491L_v2_10171889
- M0491S_v2_10174049
- M0491L_v2_10174526
- M0491L_v2_10177160
- M0491S_v2_10177738
- M0491S_v2_10182690
- M0491L_v2_10181651
- M0491L_v2_10188329
- M0491S_v2_10187073
- M0491S_v2_10194184
- M0491L_v2_10194825
- M0491S_v2_10202802
- M0491L_v2_10204089
- M0491S_v2_10208813
- M0491L_v2_10210715
- M0491L_v2_10218910
- M0491S_v2_10218689
- M0491L_v2_10222609
- M0491S_v2_10232046
- M0491L_v2_10232087
- M0491L_v2_10237705
- M0491S_v2_10237704
- M0491G_v1_10229638
- M0491G_v1_10242495
- M0491S_v2_10246916
- M0491L_v2_10247637
- M0491G_v1_10251021
- M0491S_v2_10251023
- M0491L_v2_10255842
- M0491L_v2_10261235
- M0491S_v2_10263601
- M0491L_v2_10267517
- M0491S_v2_10272599
- M0491L_v2_10273870
- M0491S_v2_10281332
- M0491S_v2_10282239
- M0491L_v2_10279528
- M0491L_v2_10288652
- M0491S_v2_10293471
Safety DataSheets
The following is a list of Safety Data Sheet (SDS) that apply to this product to help you use it safely.Q5® High-Fidelity DNA Polymerase
Q5® Reaction Buffer Pack
Q5® High GC Enhancer
Legal and Disclaimers
Products and content are covered by one or more patents, trademarks and/or copyrights owned or controlled by New England Biolabs, Inc (NEB). The use of trademark symbols does not necessarily indicate that the name is trademarked in the country where it is being read; it indicates where the content was originally developed. The use of this product may require the buyer to obtain additional third-party intellectual property rights for certain applications. For more information, please email [email protected].This product is intended for research purposes only. This product is not intended to be used for therapeutic or diagnostic purposes in humans or animals.
New England Biolabs (NEB) is committed to practicing ethical science – we believe it is our job as researchers to ask the important questions that when answered will help preserve our quality of life and the world that we live in. However, this research should always be done in safe and ethical manner. Learn more.
Licenses
This product is covered by one or more patents.
This product is licensed for research and commercial use from Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc., under U.S. Pat. Nos. 6,627,424, 7,541,170, 7,670,808, 7,666,645, and corresponding patents in other countries. No rights are granted for use of the product for Digital PCR or real-time PCR applications, with the exception of quantification in Next Generation Sequencing workflows.
For additional information or to inquire about commercial use, please contact [email protected].
Trademarks
Q5® is a registered trademark of New England Biolabs, Inc.
Other Products You May Be Interested In
The supporting documents available for this product can be downloaded below.